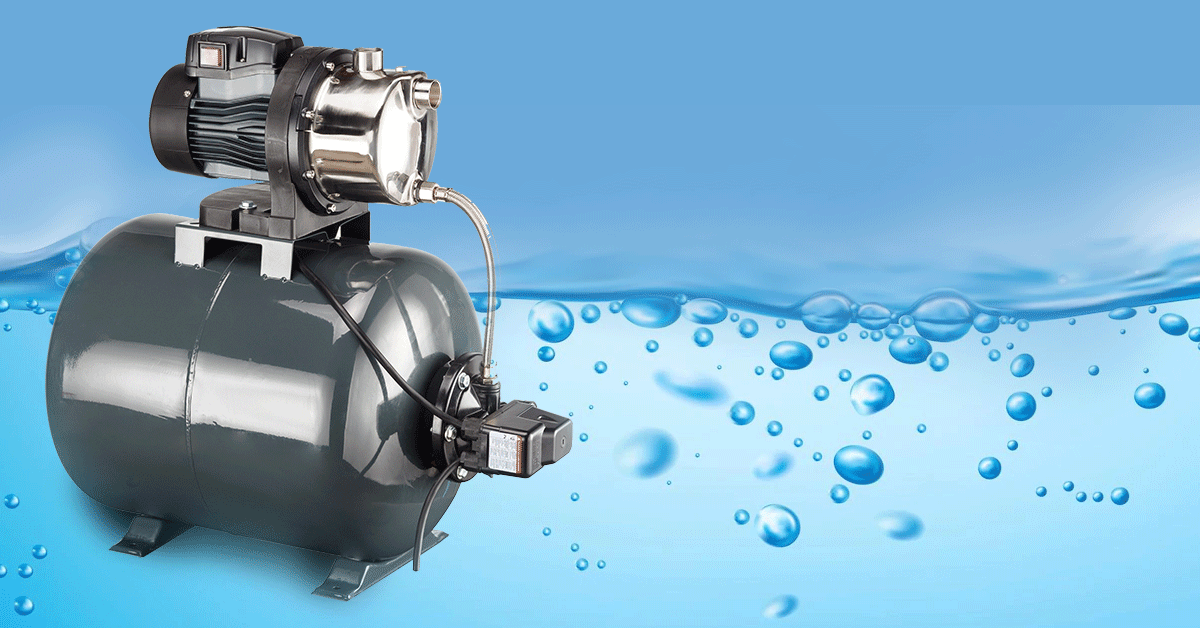
Pressure Pumps are mechanical devices that pump fluids by the use of pressure. Pumps are a critical component of water distribution systems, typically used to pump water from the ground. They are also vital components of various industries, plantation, agriculture and manufacturing.
Pressure Pumps differ in their use, construction, operations and most importantly, their performance. They are a viable alternative to wells and can be used in locations where there is no natural groundwater. The many types of Pressure Pumps and their applications are discussed in this blog.
Classification of Pressure Pumps
On the basis of operations, Pressure Pumps can be broadly divided into two types-
Positive Displacement Pumps: Positive Displacement Pumps work by trapping a fixed amount of water and then forcing it out under pressure. These pumps are often used in applications where a constant flow rate is required, such as in firefighting or industrial process control.
Reciprocating Pumps: Reciprocating Pumps use a piston to draw water into the pump chamber and then force it out under pressure. These pumps are typically used for high-pressure applications, such as in hydraulic systems.
Types of Pressure Pumps
There are many different types of Pressure Pumps, each with its own specific uses. Here, we’ll take a look at some of the most common types of Pressure Pumps and their uses.
Pneumatic Pumps
A Pneumatic Pump is a machine that uses compressed air to create a vacuum. This makes the pressure in the pump lower than the pressure in the pipe being pumped. The air is then used to create a vacuum, which can be used for various purposes, such as removing water from a boat or pumping water out of a swimming pool.
Pneumatic Pumps are used for many different applications. They have a variety of uses, from pumping water to running paint guns and more. They are used in many industries such as automotive, food processing, medical, and more.
Pneumatic Pumps can be broadly classified into two categories on the basis of operation:
- Positive Displacement: Use the suction or compression of air to create pressure.
- Rotary Lobe: Use a rotating lobe (or rotor) to move fluid from one point to another.
Types of Pneumatic Pumps-
Rotary Vane Pump: These are often found in automotive factories where they transfer gas from one container to another or from a container to a storage tank.
Diaphragm Pump: It has two parts- an airtight chamber and an elastic membrane with valves on each end. This type of pump can be found in food processing plants where it transfers liquids between containers or tanks by sucking them up through the valve.
Booster Pumps
Booster Pumps are used to increase water pressure in the pipes. They are usually used in areas where the water pressure is low or when there is a need for more water pressure.
An oil or gas well requires a considerable amount of water to produce hydrocarbons at the desired rate. The amount of water required is determined by a number of factors such as the depth below ground level, temperature, pressure in the wellbore, etc. The production rates can be increased by using Booster Pumps. These pumps help extract water from deeper levels which increases the production rate at shallow levels.
Booster Pumps can be powered by electricity or by gas. The Electric Booster Pump is usually installed on top of the well and connected to an electric source through a long wire. A Gas-Powered Booster Pump is usually mounted on a concrete base and connected to a natural gas supply line.
Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps work by spinning a rotor connected to an impeller that draws the liquid into it. The liquid is then pushed out through the pump’s discharge nozzle at high pressure. They are used for lifting water and other fluids from lower to higher elevations.
Centrifugal Pumps are one of the most commonly used types of pumps in industries such as oil, gas and water. They are also used to provide a constant supply of water for domestic and commercial uses.
Centrifugal pumps need to be installed in a way that the discharge pipe is at least one meter below the surface of the water in order to avoid any air bubbles. They should be installed with an overflow pipe so that if there is any excess pressure, it can be released without damaging the pump.
Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps are used to move fluids and solids from one place to another. The use of Hydraulic Pumps has become essential in our day-to-day life due to their efficiency and easy availability. They are used for a wide range of purposes such as irrigation, manufacturing, and many more.
Most Hydraulic Pumps get their mechanical power from an internal combustion engine or an electric motor. They receive mechanical power from these prime movers in a circular method. The pump’s input shaft is linked to the Hydraulic Pump’s gears, vanes, or pistons, which rotate or reciprocate to transmit pressure to the hydraulic fluid. The flow will occur at a rate determined by the displacement volume of the pump, and the speed at which it rotates as long as the force (pressure) exerted by the pump is sufficient.
Hydraulic pumps are used in a variety of industries, such as power generation, oil production, and construction. They are usually used in low-pressure applications.
Components of a Pressure Pump
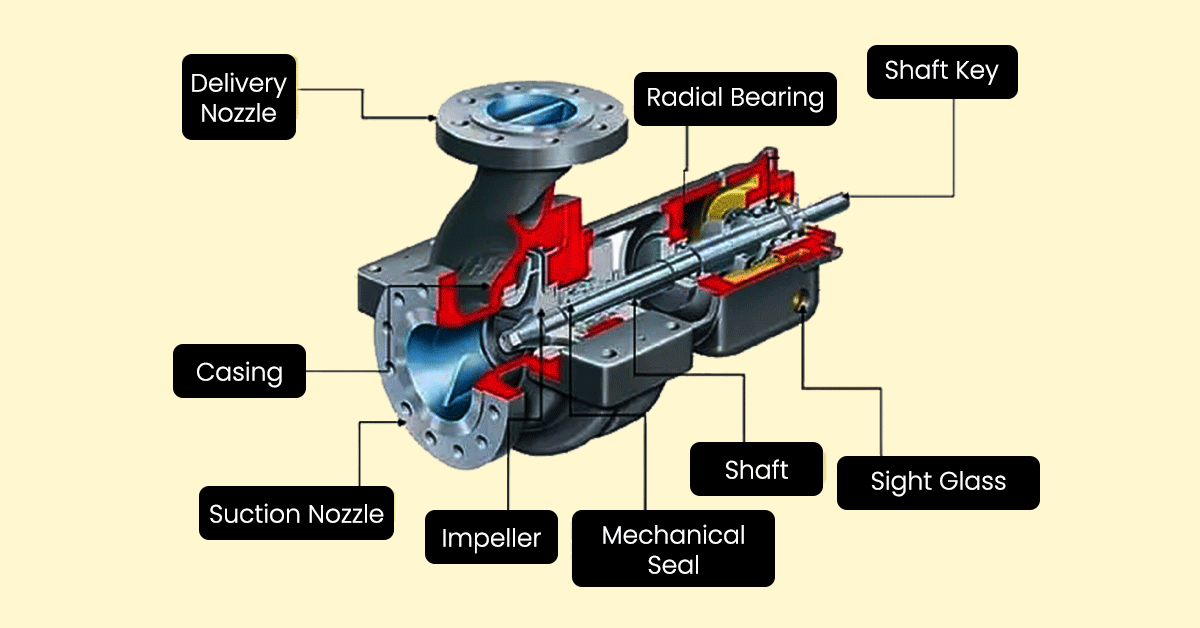
Shaft Seals: In machinery, a Shaft Seal, also known as an oil seal, is a mechanism that stops fluids from passing through a rotating shaft. When a shaft extends from an oil-filled housing (enclosure), such as a pump or gearbox, seals are required.
Casing: A Casing is a protective shell, cover, or housing that surrounds and supports the majority of the components. The casing of a Pump is primarily used to seal it, preventing leaking and, in some cases, maintaining pressure. It’s also employed to support some of the most important components, such as shafts, bearings, and so on.
Impellers: A Pump’s Impeller is a revolving component with vanes or blades that rotate and drive the fluid through the pump. A shaft connects these vanes or blades. When the impeller rotates, it transforms the energy from a source, such as a motor, into the fluid flow.
Connecting Rod: The connecting rod is a rod that connects the crosshead to the crankshaft in a reciprocating pump. It allows the crankshaft to move in a circular or rotating motion. It has a shell bearing on one end and a crosshead wrist pin on the other, and it is mounted to a crank journal.
Mechanical Seal: Mechanical seals are designed to keep a machine’s working fluid (water or oil) from leaking into the environment (the atmosphere or a body of water). It’s designed to keep liquid or gas contained in situations where a rotating shaft passes through a stationary housing – or, less typically, where the shaft is stationary and the housing spins around it.
Applications of Pressure Pumps
Pressure Pumps are used in a variety of applications, from domestic to commercial settings to being used in industrial and agricultural settings.
In the automotive industry, Pressure Pumps are commonly used to provide a steady flow of fuel to the engine. The most common use of a Pressure Pump is in an internal combustion engine, where they are used to deliver fuel to the cylinders.
They are usually found inside the tank and work by raising the pressure of air or gas inside the tank. This increase in pressure forces the liquid out through a nozzle, which can be adjusted for different flow rates.
Precautionary Measures
In spite of their high efficiency, Pressure Pumps can be difficult to maintain and often fail without warning. Maintaining a Pressure Pump to avoid failure is essential. This includes regular maintenance and repairs, monitoring the pressure of the pump system, and ensuring that the pump is not overworked or under-sized for the job at hand. Consider the following precautionary measures-
- Keep away from walls and impediments.
- Keep away from areas where heat might build-up.
- Turn it off if it becomes overheated.
- Allow it to cool down before the next use.
- Should not be used for toxic fluids as they may get stuck and cause corrosion.
- A standard water pump should never push acids, caustic materials, and combustible materials.
- Avoid pumping any substance that is viscous and beyond the capabilities of your pump.
Pressure Pumps are a critical component of water distribution systems. They are also vital to the operation of many industrial plants. Maintaining Pressure Pumps and reducing the risk of failure is crucial. One must understand the working of it and what may cause it to fail. Take preventative measures against any failure by using a checklist for maintenance, performing regular inspections, and following proper operating procedures.
Industrybuying.com is India’s leading industrial supplies platform providing an exclusive range of products. Take advantage of the buy now, pay later option with a 30-day repayment period for a seamless purchasing experience. At industrybuying.com, you can shop for Pressure Pumps at reasonable prices. The products are available across India and can be purchased using a variety of payment methods.









Average Rating